CT Scans
Computed Tomography
Exploring Computed Tomography (CT)
CT is a non-invasive medical imaging technique that uses X-ray technology to create detailed cross-sectional images of the body. These images provide valuable insights into the internal structures and organs, aiding in the diagnosis, treatment, and monitoring of various medical conditions.
Diagnostic Precision and Patient Care
CT imaging offers a wealth of information about the body, allowing healthcare professionals to visualize bones, organs, blood vessels, and soft tissues with exceptional clarity. A CT scan generates a series of X-ray images from different angles, which are then processed by a computer to produce detailed, three-dimensional images. These images help doctors to identify abnormalities, detect diseases, and evaluate the extent of injuries or illnesses.
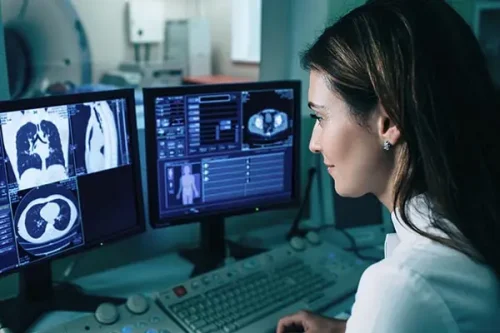
CT: a highly effective tool for diagnosing and evaluating many conditions.

Trauma
Used to assess injuries resulting from accidents, falls, or sports-related incidents. CT can quickly identify fractures, internal bleeding, and other trauma-related issues.

Cancer Imaging
Helps identify tumor size, location, and potential metastasis, aiding in treatment planning and monitoring the effectiveness of therapies.

Cardiovascular
CT angiography provides detailed images of blood vessels, assisting in the diagnosis of coronary artery disease, pulmonary embolism, and aortic aneurysm.

Abdomen/Pelvis
CT helps identify abdominal or pelvic abnormalities, such as kidney stones, liver disease, gallstones, appendicitis, and pelvic inflammatory disease (PID).
Lung Disorders
Best for evaluating lung conditions, such as pulmonary nodules, lung cancer, pneumonia, and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD).
